Sustainability 101
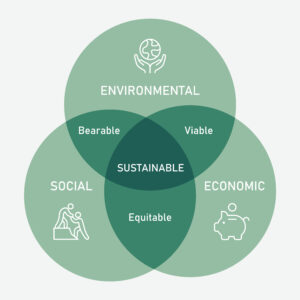
What is sustainability?
United Nations Brundtland Commission: Defines sustainability as “meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.”
What is sustainability all about?
Sustainability is about longevity and balance; If we thoughtlessly consume non-renewable resources, tap out water reservoirs, emit surplus amounts of carbon, and continue to destroy the natural ecosystem, it will have non-reversible consequences for future generations. The subjective of sustainability is about bringing the balance so that our needs are met without compromising the needs of future generations.
Why should we care?
For example, take the case of water in the western United States. Water security is a major – and often growing – challenge in the west today. The magnitude of impact is profound as water scarcity drives the bottom line for food sovereignty and food security. According to the World Bank, feeding 9 billion people by 2050 will require a 60% increase in agricultural production, which accounts for approximately 70% of all freshwater withdrawals globally.
As we continue to exploit non-renewable sources without balance, natural ecosystems such as groundwater will collapse. Therefore the subject of sustainability ensures water-stressed regions are not continued to be exploited and builds up on effective water management.
In the above case, despite severe droughts, the American West has done an excellent job in managing water scarcity through water pricing support mechanisms and drought contingency plans across the West to share water collectively. Water Sharing Investment Partnerships (WSIPs) modeled by the Nature Conservancy rely on investment capital to acquire a pool of water-use rights within existing markets. Those rights can be used to reallocate water to the environment, provide ongoing water security through lease agreements to users in the community, and generate financial returns for investors. All these efforts collectively have helped agricultural producers in the West pay relatively low water costs despite a water-stressed environment.
What is corporate sustainability?
The term “corporate sustainability” refers to an approach to conducting business that creates sustainable, long-term shareholder, employee, consumer, and societal value by pursuing responsible environmental, social, and economic (or governance) strategies.
Difference between Sustainability & ESG ?
ESG is considered a part of the much larger umbrella of sustainability.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) is a term used to represent an organization’s corporate financial interests that focus mainly on sustainable and ethical impacts. Capital markets use ESG to evaluate impacts on organizations’ future financial performance.
Take the example of water scarcity. Private Equity firms investing in agricultural lands will have impacts on water stress incorporated into the cost of capital calculations through ESG to safeguard against operational risk and ensure the longevity of the investments.


